Abstract
Introduction
Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody designed against the CD20 receptor displayed on the surface of B cells and used to treat nearly all B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs). It was the first monoclonal antibody approved in oncology and it has improved outcomes in all B-cell malignancies, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. In recent years, the approval of several rituximab biosimilar molecules worldwide has further improved the patients' access to this drug, promoting cost-effective treatment. Biosimilar molecules are defined by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA) as a biological molecule product highly similar to the approved reference product with no clinically meaningful differences.
The multicentric double-blind international prospective pivotal study RTXM83-AC-01-11 led to the approval of rituximab biosimilar RTXM83. The study evaluated the efficacy, pharmacokinetics (PK)/pharmacodynamics (PD), safety, and immunogenicity profile of RTXM83 (rituximab biosimilar) vs reference rituximab (Mabthera®), both with CHOP, as first-line treatment of Diffuse-Large-B-Cell-Lymphoma (DLBCL). Participants from both arms received 6 cycles of R-CHOP followed by a 9-month follow-up (Candelaria et al., 2019). Data regarding long-term efficacy and safety events are of great relevance to demonstrate the strength of the clinical response and deepen the confidence in the use of biosimilar molecules. Here, we present a partial data analysis regarding the long-term safety of 11 patients included in this retrospective observational study.
Aim
This national retrospective observational study aimed to collect long-term data regarding safety e efficacy outcomes from Brazilian participants of the pivotal study RTXM83-AC-01-11 which led to the approval of biosimilar rituximab (Vivaxxia®) in Brazil.
Methods
All 28 Brazilian participants that were randomized and completed the phase III study RTXM83-AC-01-11 were eligible for this observational, retrospective LB2002 study (Clinical trial information: NCT04928573). Participants were invited to sign the consent form and share the disease history collected since their randomization on the RTXM83-AC-01-11 study. This partial analysis shows the participants' demographic and baseline characteristics, baseline disease characteristics, and the long-term safety data collected and monitored until July 1st, 2022. The long-term safety endpoint was the frequency of serious adverse events of interest, and we considered in this analysis the time between the end of the RTXM83-AC-01-11 study and the consent date of the LB2002 study.
Results
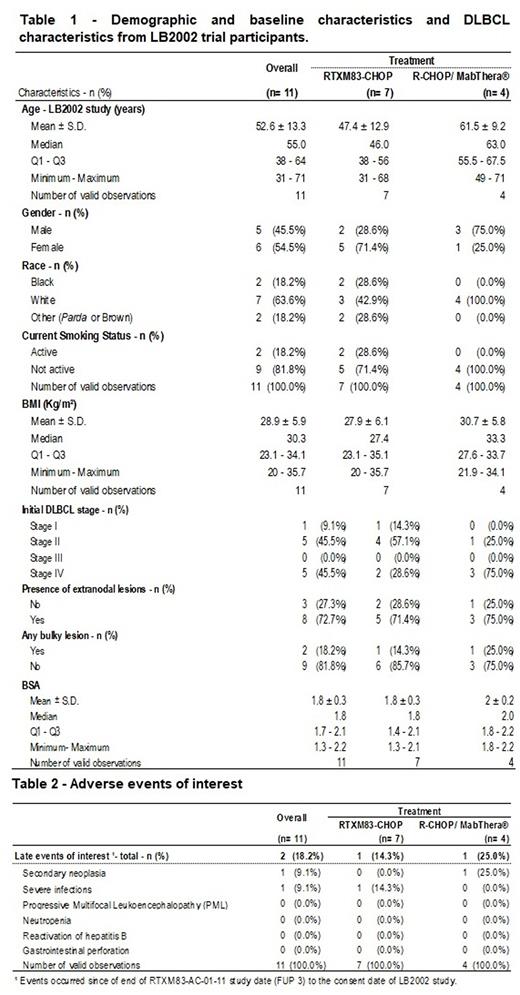
The intention to treat (ITT) and Safety populations comprised the partial analysis of the same 11 participants, 7 of them (63.6%) treated with biosimilar RTXM83 plus CHOP and 4 (36.4%) with Mabthera® plus CHOP. The median study follow-up time was 73.3 months, considered in this analysis as the time between the randomization of RTXM83-AC-01-11 study participants and the consent date of the LB2002 study. Overall, participants' median age was 55 years old, 63.6% were white, 54.5% were female, 18.8% were active smokers and the body mass index (BMI) ranged from 20 to 35.7 Kg/m² (Table 1). Regarding disease characteristics, 9,1% of the overall participants were classified as stage I DLBCL, 45.5% stage II and IV at the time of diagnosis. Of all 11 participants, 72.7% displayed extranodal lesions, and 18.2% had bulky lesions with a median body surface area (BSA) of 1.8 m2 (Table 1). As for prognostic factor and performance status, participants were classified with IPI 1 (45.5%) and 2 (54.5%), ECOG 1 (72.7%) and 2 (18.3%). The long-term safety analysis from the 11 participants revealed that 2 participants (18.2%) suffered from serious adverse events (SAE) among those of interest listed in Table 2. One participant of the RTXM83-CHOP arm had a SAE classified as severe infection related to rituximab (hypogammaglobulinemia). From the R-CHOP/MabThera® 1 participant displayed 1 SAE (secondary neoplasm) with a possible relationship to rituximab.
Conclusion
The partial analysis of the LB2002 has demonstrated thus far the safety profile of the biosimilar RTXM83 (Vivaxxia®) in the Brazilian population is consistent with the known safety profile of rituximab.
Disclosures
Bridi:Libbs Farmacêutica: Current Employment. Ferreira Cardoso:Libbs Farmacêutica: Current Employment. Bonilha Fernandes:Libbs Farmacêutica: Current Employment. Gonzaga Lapa:Libbs Farmacêutica: Current Employment. Farias:MSD: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Sanofi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; PPD: Research Funding; Libbs Farmacêutica: Research Funding. Salvino:Libbs Farmacêutica: Research Funding. Higashi:AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Libbs Farmacêutica: Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Giacon:Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; MSD: Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Agios: Research Funding; Libbs Farmacêutica: Research Funding. Pereira:Zodiac: Honoraria; Roche: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding; Celltrion: Research Funding; Sandoz: Honoraria, Research Funding; Eusa: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Libbs Farmacêutica: Honoraria, Research Funding. Delamain:Libbs Farmacêutica: Honoraria. Castilho:Libbs Farmacêutica: Current Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal